In response to escalating inflation rates, central banks across the globe have adopted an increasingly aggressive stance, opting for sharp interest rate hikes. This strategy, while aimed at stabilizing prices, has raised concerns about the broader economic impact, including potential slowdowns in growth and disruptions to financial markets. Understanding the reasons behind these actions and the potential long-term consequences is key to grasping the current economic climate.
The Surge in Inflation: A Global Challenge
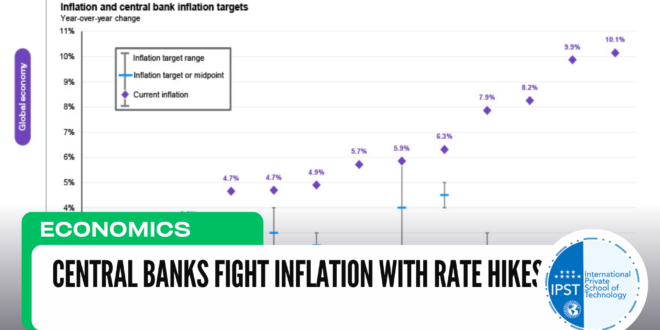
Over the past few years, many economies, including those in the United States, Europe, and emerging markets, have experienced rising inflation, driven by factors such as supply chain disruptions, soaring energy prices, and pent-up demand following the pandemic. Central banks are now tasked with controlling these inflationary pressures to prevent economies from overheating and to protect the purchasing power of consumers.
Why Are Central Banks Raising Interest Rates?
Interest rate hikes are the primary tool central banks use to curb inflation. By raising rates, central banks make borrowing more expensive, which can help reduce spending and slow down the economy. This decrease in demand can put downward pressure on prices, thus addressing the inflationary surge.
The U.S. Federal Reserve, the European Central Bank, and other major central banks have significantly raised rates in recent months. These actions, while necessary to bring inflation back under control, are not without risks. Higher rates can slow economic growth and potentially push economies into recession if not managed carefully.
Global Economic Impact of Rate Hikes
The effects of these rate hikes are already being felt across global markets. Stock markets have shown increased volatility, as investors weigh the risks of tighter monetary policies. Consumer borrowing costs have risen, which could affect housing markets and personal finance, particularly in sectors reliant on credit.
In addition, emerging markets may face heightened challenges. Higher interest rates in developed economies can result in capital outflows from emerging markets as investors seek higher returns in safer, developed economies. This can lead to currency depreciation and increased financial instability in some regions.
Outlook: Will Aggressive Rate Hikes Work?
The outlook remains uncertain. Central banks are walking a tightrope, aiming to balance curbing inflation without stifling economic growth. While interest rate hikes have shown some success in cooling inflation, it remains to be seen whether they will trigger a broader slowdown or even recession.
Experts predict that central banks will continue to hike rates in the near term, depending on how inflation evolves. However, the timing and extent of future hikes will be contingent on economic data, particularly in relation to inflation and unemployment figures.
Conclusion
As central banks continue their battle against inflation, the global economy faces a delicate balancing act. Aggressive rate hikes are a necessary tool, but they carry risks of slowing growth and creating market instability. The coming months will be crucial in determining the effectiveness of these measures in achieving a sustainable balance between inflation control and economic stability.
 International Private School of Technology المدرسة الدولية الخاصة للتكنولوجيا Private School مدرسة خاصة للتكوين المهني
International Private School of Technology المدرسة الدولية الخاصة للتكنولوجيا Private School مدرسة خاصة للتكوين المهني